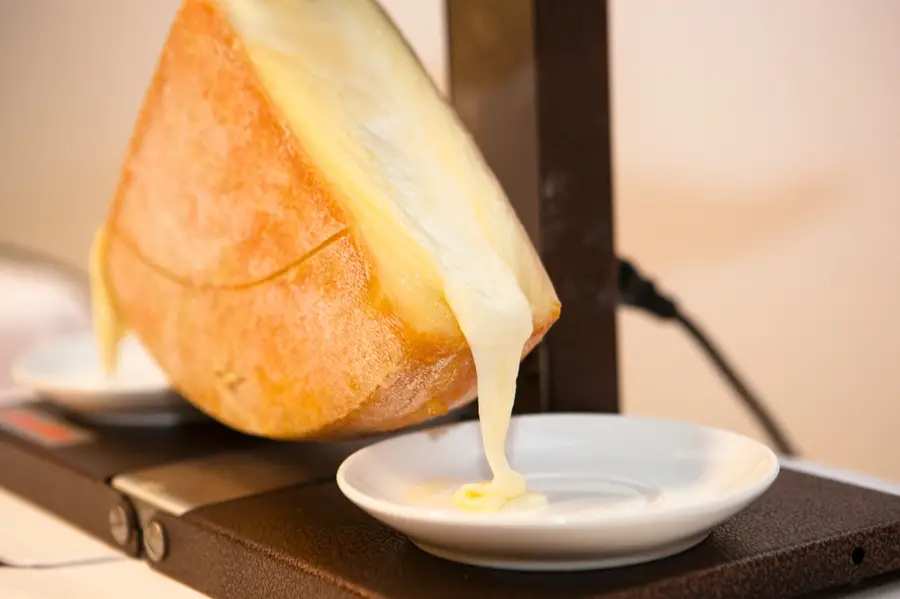
Who hasn’t been to a “Raclette” dinner party and tasted the delicious Raclette cheese melted over potatoes accompanied by hams and a good wine? If you haven’t had the opportunity, don’t worry, here we explain everything you need to know about this cheese so that you can buy it from your nearest cheese monger and start your journey to Savoie through your palate. First it is worth mentioning that there are several Raclette cheeses, both in France and Switzerland. This article will concentrate on Raclette de Savoie PGI, which is the French cheese with a protected geographical indication. According to the “Institut national de l’origine et de la qualité“…
Raclette de Savoie PGI is a raw cow’s milk cheese, pressed and uncooked. Its body is soft and melting, yellowish white in color. It is made in moulds 30 cm in diameter, 7 cm high and weighs 6 kg. The skin is smooth, yellowish to orange in color. Its flavor is balanced and typical with a milky aroma.
Raclette cheese is nowadays one of the most famous cheeses in the world and is eaten with family or friends. The French eat it all year round, but especially during the winter season. Although it can be eaten at any time, the inhabitants of the country of cheese make the most of it for important dates.
Where was Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese created?
Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese, as its name suggests, comes from the French departments of Savoie and Haute-Savoie. In the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in the south of France.
Apparently, there are records that melted cheese was eaten in the Alpine region since medieval times, and from the Renaissance onwards it was mixed with potatoes.
In the beginning, Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese had no name, it was just a cheese developed in the Alpine region that had specific characteristics, ideal for melting. Eventually it was called Raclette cheese because in French the word “racler” means to scrape, a word given by the fact that the cheese is commonly melted and then scraped to be placed on bread as in its beginnings or now on potatoes as it is commonly eaten by the French in winter. Interestingly, this cheese is very versatile and can be eaten either melted or cold in various recipes that we will tell you about in another article.
It took many years for Raclette cheese to become famous, until, thanks to the technological advances of the train and cable car, thermal resorts and mainly ski resorts were developed in the Alpine region, making winter activities a favorite destination during this exciting time of the year. In this way, restaurants and hotels in the region offered tourists local dishes based on the region’s cheeses. These same tourists on their return home wanted to continue eating these cheeses such as the Raclette de Savoie IGP cheese or the Reblochon cheese commonly eaten in tartiflette.
Not to be forgotten is the impulse that Switzerland gave to the cheese, being also a tourist center during the winter helped a lot to the joint history of the cheese. Because Raclette cheese is an Alpine cheese, Switzerland has its own specific cheese, the Raclette du Valais AOP, which, unlike the French cheese, which has the “indication géographique protégée”, the Swiss cheese has the “apellation d’origine protégée”. Although the origins of the cheese may have been the same since medieval times, the respective cultures, and culinary tastes of the two countries have contributed to their differences over the years. Such as, for example, the breeds of cow used in Switzerland are d’Hérens, Brunes, Simmental, Red Holstein and Tachetées noires.

Besides the history of the Alpine region, what helped the democratization of the consumption of Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese, was the fact that Marc Grégoire, founder of Tefal, motivated by his previous success with frying pans, together with the stakeholders of Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese, developed the instrument that would later get the name of the cheese and allowed the consumption of melted cheese, because in this way everybody could have their melted cheese quickly and easily at home.
Does Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese with flavoring exist?
Raclette de Savoie IGP cheese is always eaten “nature”, neither smoked nor flavored. Although there is French raclatte cheese which does not have the IGP label and therefore has certain variations in its manufacture, flavors and aromas have been added, such as smoked aroma.
What do the cows that provide the milk to produce Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese consume?
During spring and summer, they eat fresh grass and during winter they always eat local fodder and non-GMO cereals. Moreover, these cereals must not make up more than 0.9% of their feed.
Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese is produced from milk from local breeds of cows, such as Montbéliarde, Abondance and Tarine. These cows are fed in a regulated way to maintain their quality and their ancestral methods.

How long does Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese mature?
Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese is matured on wooden boards in 6kg ripening wheels for at least 8 weeks. According to “Le Ministère de l’agriculture et de l’alimentation”, up to 3406 tons of cheese were produced in 2020. That is 567 667 units of the ripening wheels.
Since when has Raclette de Savoie PGI been a protected geographical indication?
Raclette de Savoie PGI was awarded the “Protected Geographical Indication (PGI)” status in January 2017. Thanks to this label, the cheese can offer a guarantee of origin and therefore of quality through a production process that includes the cow’s feed, the breed of the cow, and the maturing process in a way that preserves the ancestral methods.
Beyond the methodology, it also indicates the region in which it is produced, as this implies a quality given only by the territory. For example, tomatoes harvested in Spain are not the same as those harvested in Italy or France. Although they may be the same type of tomato, they will have a totally different taste and aroma. In the case of the raw material for cheese, i.e. milk, the same situation applies, as the grass in Savoie is not and will not be the same as the grass in other regions of France or other countries. Therefore, the cow fed in that region provides a milk with unique and irreplaceable characteristics. This is because the Alpine region is a mountainous region with altitudes between 200 and 2500 metres, which results in a particular irreplaceable climate.
Is it safe to eat raw Raclette de Savoie PGI cheese?
Although consumption is entirely suitable for healthy adults. The health authorities recommend to the fragile population not to consume raw milk and raw milk cheese. Among raw people they refer to:
- Pregnant women.
- Immunocompromised persons.
- Children under 5 years of age.
More details can be found on the website of the “Ministère de l’agriculture et de l’alimentation“.
I already feel like eating Raclette cheese before the winter is gone.





